Curriculum development is a continuous process that keeps evolving to cater to changes in the classroom, the influx of technology, and student evaluations. As a result, it also isn’t a process that works in isolation, as it needs almost consistent inputs to refine it year after year.
What, however, is the exact relationship between curriculum development and evaluation? What is the difference between curriculum development and curriculum evaluation? How does the latter affect the former?
This article will dive into the evaluation process, its different types, and its purposes to demonstrate the various ways it influences the design of student curriculums.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Curriculum Evaluation?
- The Key Purpose Of Evaluation
- What Are The Criteria For Curriculum Evaluation?
- In Conclusion
What Is Curriculum Evaluation?
Curriculum evaluation refers to analyzing the effectiveness of the resources and tools, such as technology, used for instruction in the K12 curriculum, among others. The evaluation is conducted based on data and trends identified by the measuring and testing process.
The evaluation consists of two parts. The first involves assessing student performance vis-a-vis the goals of the curriculum to see whether the students are meeting the standards expected of them. It also goes on to evaluate their performance.
On the other hand, the second part of the process involves assessing the tools used to instruct students, along with the teacher’s performance. While the first part of the process can be done almost daily, the second part often takes place over an extended period of time.
However, both help curriculum developers understand its effectiveness, providing them with tangible evidence to use to improve it for the future.

The Key Purpose Of Evaluation
Evaluating the success of the curriculum is key to its development and improvement over time. This is the process of conducting formative and summative assessments of the curriculum, its associated teaching methodologies, and the tools used to impart education to ensure the key goals are met.
Digital curriculum providers continuously evaluate curriculums to make them more refined and comprehensive. Its role is to provide objective data to check whether or not the curriculum is benefiting its intended beneficiaries. This helps tailor objectives and goals to ensure that the curriculum helps attain the most relevant ones.
It’s a crucial element of curriculum development and evaluation, as the K12 education market is set to grow to a whopping $525.7 billion by 2031. This spells the need for continuous improvements to ensure the curriculum remains relevant.
When looked at closely, evaluation data serves several purposes to help with curriculum development. These include:
- It helps assess improvements at the student level, such as what skills and knowledge they’ve acquired, where the child could need help, what kind of help they need in particular, and what tools can be used to help each student’s development.
- In the classroom, evaluation data can help analyze which objectives in the curriculum have been met, whether the tools and methods used are relevant, and if any re-teaching is needed.
- At the school level, it can help curriculum developers understand if there is less or more emphasis on an individual class, whether the overall objectives are being met, and if any areas require more attention throughout the school. It also helps assess the school’s effectiveness as a whole.
At its crux, evaluation helps understand the curriculum’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing its developers to use objective data and make necessary improvements.
However, the evaluation results will prove good if schools and institutions adopt certain best practices when developing curriculums.
What Are The Criteria For Curriculum Evaluation?
Several criteria come into play when evaluating a curriculum’s success. However, some objectives aren’t easy to assess when evaluating, while others are. An example of the former includes assessing someone’s honesty and integrity via a written examination.
When evaluating the success of a curriculum, three main domains are taken into consideration. These are the affective, cognitive, and psychomotor domains. These are described below.
- Affective: The affective domain assesses value traits such as motivations, integrity, interests, and honesty, among others.
- Cognitive: This domain assesses intellectual skills across the board.
- Psychomotor: The psychomotor domain helps the brain coordinate a physical task, which can often be difficult to assess in terms of its logistics.
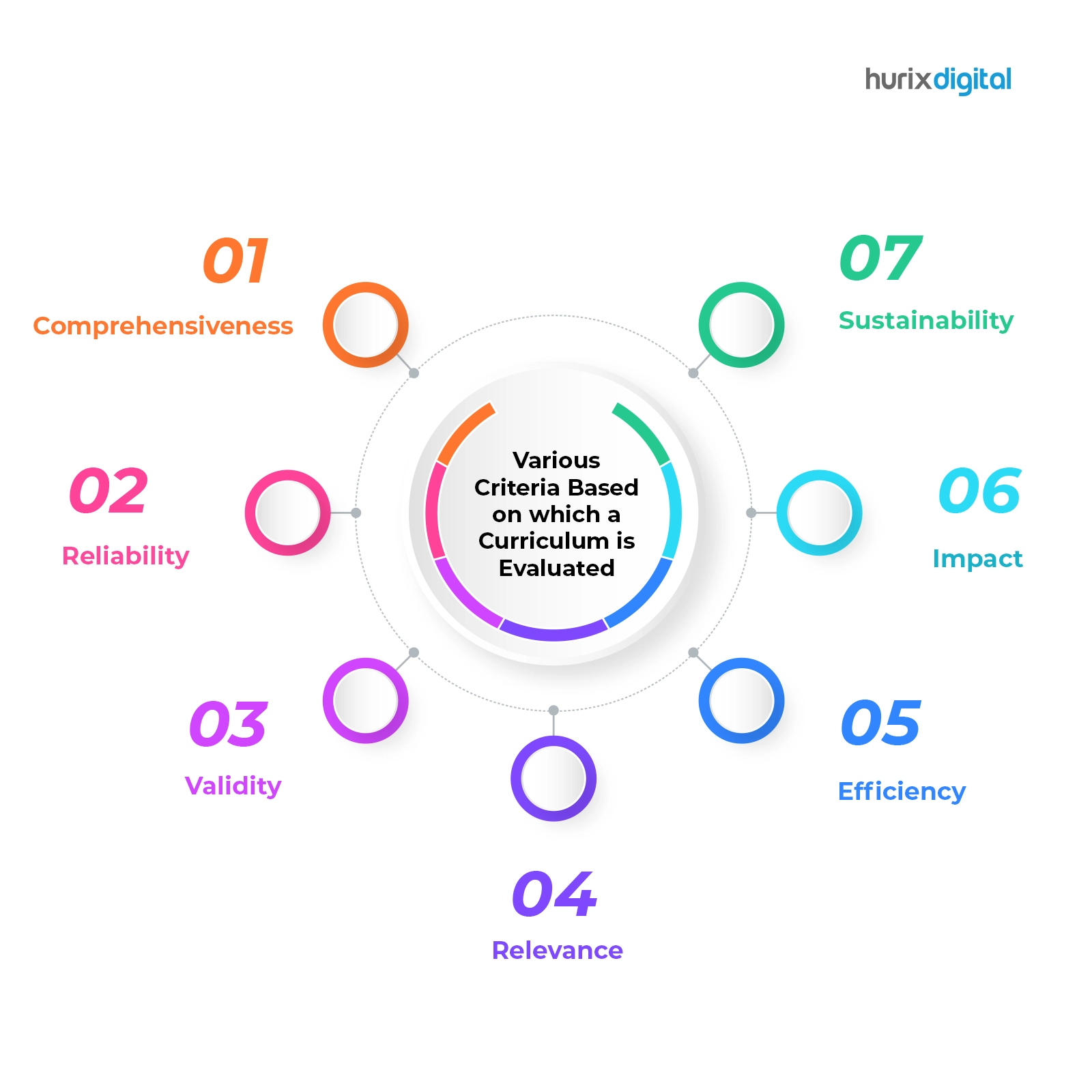
The various criteria based on which a curriculum is evaluated are described below.
1. Comprehensiveness
Comprehensiveness is perhaps among the most important criteria for evaluating a curriculum. Given that it’s only the cognitive aspect that’s often assessed, the aim of being comprehensive is also to ensure that the evaluation covers the administrative and general aspects of the education system.
This involves assessing the methods of instruction to see whether or not they’ve proved to be effective. It also involves evaluating individual learners to understand what their needs are and how the curriculum can better meet them.
Further, with advancements in AI, and the overall investment in AI technology in education set to grow to $3.68 billion this year, curriculums need to include such tools to be more comprehensive.
2. Reliability
A reliable curriculum is one that offers consistent results irrespective of the time. This is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating curriculums.
3. Validity
Different educational instruments are used to measure different functions. For example, examinations and quizzes are meant to assess how well a student or a group of students have grasped the concepts taught to them. Validity is a test of how well these instruments are at evaluating the functions they’re supposed to assess.
4. Relevance
Relevance measures how ‘present’ the curriculum is given the larger context in which it is developed and provided to students. These include national and state priorities, educational goals, and so on.
5. Efficiency
Different parts of a curriculum make use of different instruments to teach a concept. Efficiency is a measure of efficient these instruments or resources are in meeting the goals laid down in the curriculum.
6. Impact
A curriculum’s positive or negative impact is measured in terms of its effect across various aspects, be it social, environmental, economic, and more. It’s also a measure of the impact on groups or communities as a whole.
About 63% of respondents in a survey also stated that data management and analytics solution is a priority in K12 education. It goes a long way in evaluating the curriculum’s overall impact.
7. Sustainability
The broader goal of education is to be able to pass on knowledge and ideas from one generation to the other. It’s the foundation of what results in the dissemination of ideas, values, and culture over the years.
Sustainability measures how well the curriculum helps build skills that help with life-long learning.
In Conclusion
Curriculum development is not a process that can function in complete isolation. Just like any policy at the governmental level requires checks and vigils to ensure it meets its intended goals, the same applies to curriculums as well.
Evaluation plays a key role in ensuring that curriculums meet the abovementioned criteria, including comprehensiveness, relevance, validity, reliability, efficiency, and more.
It also serves several key purposes, such as assessing student-level performance, analyzing each student’s needs and how they can be met, assessing the efficacy of the curriculum in meeting its goals, and checking whether the tools and resources used are the right ones.
Developing a curriculum that meets all the criteria mentioned above involves working with the best K12 curriculum development companies, as they consider all the criteria mentioned above to give you a detailed evaluation of any potential changes to be made.
Also Read – The Key Principles of Effective Curriculum Development