Let’s start with what is competency-based curriculum!
Competency-based learning is a well-known approach to education that primarily focuses on the student’s demonstration of their desired learning outcomes as central to the overall learning process. It is largely based on the premise of a student’s progression through the curriculum (as their competencies are proven) at their speed, pace, depth, and other similar parameters.
Rather than just focusing on what learners are expected to learn in terms of traditionally defined subject content, a competency-based model of curriculum design emphasizes the various complex outcomes of a learning process such as skills, knowledge, and attitudes to be applied by learners.
Also Read: Reasons to Invest in Custom Scenario-based eLearning
Table of Contents:
- Benefits of competency-based learning
- Steps to develop a competency-based curriculum
1. Development or identification of general competencies
2. Organizing competencies into specific themes
3. Establishing criteria for performance
4. Creating learning experiences
5. Assessing competency
6. Evaluating the effectiveness of the curriculum - In conclusion
Benefits of competency-based learning
- The approach is flexible as learners can move at their own pace
- Supports students with diverse literacy levels, knowledge backgrounds, and other related aptitudes
- Students are far better prepared with the necessary skills to succeed as adults
- Allows students to take responsibility for their education
Steps to develop a competency-based curriculum
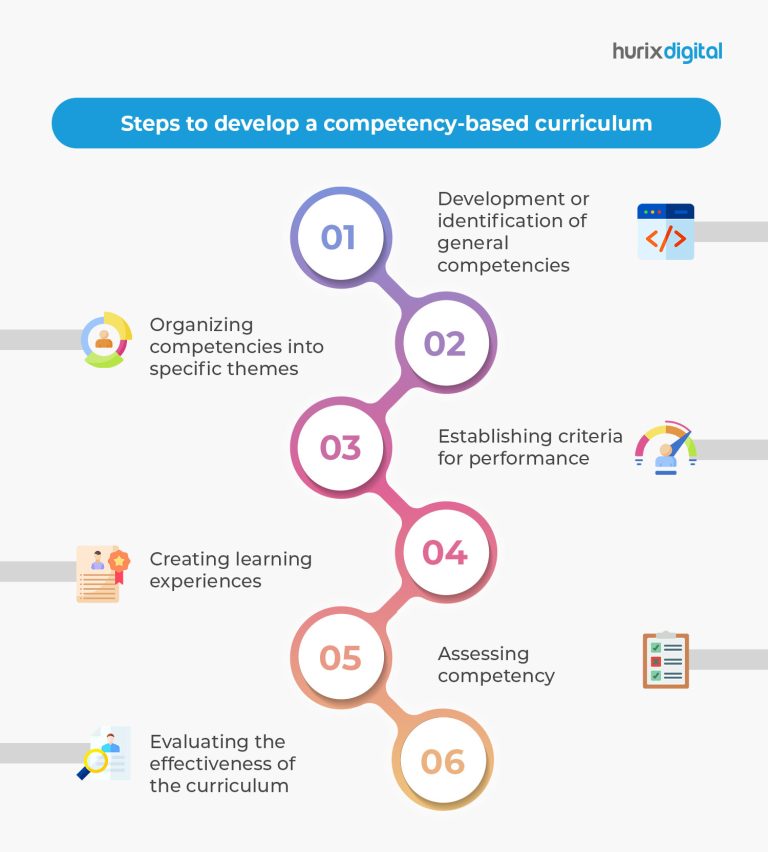
Designing various components of competency-based curriculum is largely about creating varied opportunities for students that allow them to demonstrate important skills in authentic contexts.
The process of competency-based curriculum design typically involves the following steps –
1. Development or identification of general competencies
The first step in developing this kind of curriculum is to identify and map the general competency areas using a wide range of sources of information and techniques to collect them. These competencies offer a framework based on specific performance outcomes to develop a curriculum and measure performance.
The sources you can use include subject matter experts, high-performing students, educators, online textbooks, articles, and other resources. The techniques that you can use include focus groups, surveys, readings, and observations.
Although each student has their own unique set of competencies, in general, these competency maps are created by observing and interviewing top-performing students so that their performance can be captured as a list of core competencies (knowledge and abilities).
2. Organizing competencies into specific themes
In the next step, you have to define specific competencies in each general area. Developing an accurate and precise description will make the next steps much easier in the process of curriculum development.
To be able to fully define a competency, reflect thoroughly on its composing elements. For instance, for public speaking, consider both delivery (body language, voice) and content (language, persuasion, organization).
At this point, also consider the following questions to help you frame your goals around a competency-based curriculum:
- What are the broad advantages of competency-based learning and why are these important?
- What are the specific benefits it can offer your institution?
- What are some of the unique goals of your institution around this?
- How will you measure the success of this initiative for your institution?
- What is the content required to support the development of the specific competency in the curriculum?
- What are the instructional strategies and methods that are most effective in developing the competency?
3. Establishing criteria for performance
For each of the competencies, create the standards or rubrics by which you can measure the competence. Make sure to describe several levels that define positive and negative competence at this step. This will help you gauge the effectiveness of the curriculum and find out what works well and what doesn’t for the learners.
4. Creating learning experiences
Once you have defined competencies and criteria for outcomes, think about how students will demonstrate these skills via learning experiences. There are multiple ways to demonstrate these skills, so make sure that the products of the assessment – the students’ work – are varied and interesting.
The ideal way to recognize a competency-based learning experience is to thoroughly look at the work the students produce and the learning environment in which they produce it. For instance, teachers and students use the identified competencies and outcomes to engage in regular, open reflection on learning.
The idea here is to empower students to be real learning designers. Allow them to use the rubric to design a learning experience where they can demonstrate the learning outcomes and give them the responsibility of the planning, execution, and presentation of their work for assessment.
5. Assessing competency
A successful example of competency-based curriculum will enable students to apply and execute knowledge, skills, and abilities desired by the industry in general.
To bridge this gap between industry and academia, there is a need for a structured process of connecting KSAs to assessment. When assessing competencies, you need to address two important questions including –
- Have the students acquired the specified competencies by the end of the program?
- If yes, was this acquisition of the competencies a result of the program?
You need a variety of assessment methods here for assessing the program-level competencies including formative and summative assessments as well as self-assessment.
6. Evaluating the effectiveness of the curriculum
As the curriculum gets implemented and students begin to develop their competence in various areas, there will be a lot of likely changes.
It is, therefore, important to evaluate the curriculum’s efficacy to deliver competence, refine it to better meet the desired goals, and then repeat the process to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
In conclusion
A relatively modern approach to learning design, competency-based learning is gaining rapid popularity among educational institutions since it shows a definite improvement in job-oriented skills for students.
By identifying the skills, knowledge, and abilities necessary for achieving success in any industry or occupation the students choose to pursue, the approach can be used to develop and evaluate a competency-based curriculum. It ensures that students are better prepared to face work-related challenges later in life.
Apart from helping students develop and demonstrate mastery over a topic, an example of competency-based curriculum also builds a culture of equity and inclusivity and adequately prepares students for life.
Related Article: How does Competency Based Education Prepare Students for Employment
Hurix Digital helps educational institutions develop a competency-based approach to curriculum development. Our SMEs and instructional designers work collaboratively to ensure an enriching, engaging, and experiential experience for the learners as they master skills. Get in touch with us if you want to know more about our competency-based content development services, or email marketing@hurix.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can a competency-based curriculum be implemented in all subject areas?
A. Certainly, a competency-based curriculum can be adapted and applied to diverse subject areas and disciplines, necessitating adjustments to align with specific learning outcomes.
2. How does a competency-based curriculum prepare students for future careers?
A. Through emphasizing practical skills and abilities relevant to the workplace, a competency-based curriculum readies students for future careers. It aligns with industry needs, equipping students with the necessary competencies for success in their chosen fields.
3. How does a competency-based curriculum support lifelong learning?
A. A lifelong learning journey is fostered through a competency-based curriculum, which develops essential skills, promotes a growth mindset, and enables students to acquire new competencies, adapt to challenges, and engage in continuous practical learning.
4. What role does the teacher play in a personalized, competency-based classroom?
A. The teacher supports personalized learning by providing guidance, resources, and individualized instruction tailored to each student’s needs. They help students set learning goals, monitor progress, and offer targeted support to ensure competency mastery.
5. How does a competency-based curriculum support student learning?
A. A competency-based curriculum supports student learning by allowing learners to progress at their own pace, demonstrating mastery before moving on.










